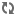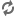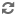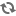The collection contains architectural photographs, sketches, and designs documenting the work of Nicolás Arroyo and Gabriela Menéndez, active in Cuba from the 1940s to 1950s.
Bio:
Nicolás Arroyo Márquez (1917–2008) and Gabriela Menéndez Garcia-Beltran (1917–2008) were architects from Havana, Cuba, who are remembered as pioneers of modernist Cuban architecture of the 1940s and 1950s. Additionally, Arroyo, who was known as ‘Lin,’ served in the government of Fulgencio Batista as Minster of Public Works from 1952-1958, and was also the Ambassador to the United States in 1958 before Fidel Castro rose to power. Arroyo and Menéndez both obtained their degrees in architecture from the University of Havana in 1941; Eduardo Castellanos, cousin of Arroyo, stated that "The two were students who disputed the top positions of their class, because they both had outstanding intelligence and passion for the architecture'' (qtd. in Cancio Isla). Though rivalling each other in academic vigor, the pair fell in love and married in December 1942, staying together until they died just three days apart – Gabriela on July 10th 2008 and Nicolás on July 13th 2008 – leaving behind one son.
After their marriage in 1942, Arroyo and Menéndez formed their architectural firm, ‘Arroyo y Menéndez,’ described by Florencia Peñate Díaz as “una de las más prestigiosas de la República / one of the most prestigious of the Republic” (79), thus initiating the beginning of their irrevocable impact on the landscape of contemporary Cuba. As a team and as individuals, Arroyo and Menéndez’s legacies transcend merely the buildings they left behind. The couple both participated in the Technical Group of Contemporary Studies (Agrupación Técnica de Estudios Contemporáneos, ATEC), which eventually led to Cuba’s incorporation into the International Congress of Modern Architecture (CIAM). The congress was founded in 1928 with the purpose of creating a space for the cross-fertilization of ideas pertaining to architecture as both an art form and a field of academic study; it disbanded in 1959. Victor Pérez Escolano relates, “In Cuba, the creation of the Technical Group of Contemporary Studies (Agrupación Técnica de Estudios Contemporáneos, ATEC) reflects how architects who had innovative ideas, but were looking for an alternative to the more severe avant-garde groupings, could gather” (88). According to the late architect Nicolás Quintana, who worked on an urban planning initiative created by Arroyo as a part of the Junta Nacional de Planificación (Board for National Planning), “Arroyo’s [and no doubt Menéndez’s] influence was decisive in putting Cuba on the CIAM map” (qtd. in Cancio Isla) from 1947 onwards when Arroyo attended the 6th CIAM congress held in England.
Despite leaving Cuba in 1959 when Fidel Castro came to power, the couple had already left their mark on the landscape. Most notably, in collaboration with Los Angeles architect Welton Becket, in 1958 the pair designed what was then known as the Havana Hilton Hotel, currently Habana Libre-Guitart. Towering over the business district, El Vedado, Havana, the “capital’s modernist emblem,” (321) as described by Giuliana Bruno in “Havana: Memoirs of Material Culture,” is the twenty-seven story that occupies an entire city block. At the time it was built, it was the tallest building in Latin America and the Caribbean and attracted flocks of celebrity guests. The building was designed and built under the guidance of Fulgencio Batista, as Peter Moruzzi, author of Havana Before Castro writes, “Batista considered the Habana Hilton among his proudest achievements, its huge blue-lit rooftop ‘Hilton’ name announcing to the world that the eminent Conrad Hilton had confidence in Cuba’s future – that the country was a safe place in which to invest – and that tourists could now find in Havana the modern comforts they expected in a top international resort” (qtd. in Perur). However, the hotel’s status as the unrivalled touristic site of modern Havana was not to last as Castro moved into the building and nationalized and renamed it in 1960. Bruno narrates, “The hotel still features in the lobby evidence of the passage of Fidel, who turned a touristic site into home while choosing a mobile home for a revolutionary symbol” (321). For three months, Continental Suite 2324 was his main headquarters and on January 19th1959 he gave his first press conference in the hotel’s ballroom.
In addition to the Havana Hilton Hotel, which was the last building designed in Cuba under the ‘Arroyo y Menéndez’ banner, the pair of architects left behind other notable buildings before departing the island for good. In 1954 Cuba’s first modernist church, named San Pablo, was completed; despite the fact that it is currently used as a warehouse, at the time the building was notable for its bell tower clad in concrete lattice work. In the same year building work began on the National Theater of Cuba, which was a Cubist concrete design; the structure, however, remained unfinished and did not open to the public until 1979. The 1955-1957 Sport’s Palace, or “Coliseo,” (Coliseo de la Cuidad Deportiva) is a circular arena designed to accommodate fifteen thousand spectators. Tony Perrottet describes the building as “A circular covered arena whose Jet Age design resembled a white flying saucer” (317). Also, though never built, the 1956 “Las Palmas” Presidential Palace was designed by José Luis Sert and his team alongside Menéndez for Batista’s “Plan Piloto.” The design warrants mention in Eduardo Baez’s Cruelty and Utopia: Cities and Landscapes of Latin America and is described as: “a dream-like presidential palace that would have been located between the fortresses of the Morro and the Cabaña. It commanded an impressive view of the whole city, a transparent and clear building that contrasted with the dark and crooked political power within” (141). The Presidential Palace, alongside Menéndez’s other important designs and the fact that during the time Arroyo was serving as Minister of Public Works she ran the company office, led Victor Deupi, co-curator of the recent exhibition in Miami, Cuban Architects at Home and in Exile, to say that her and other female architects’ work “stands on its own” (qtd. in Delson). Deupi’s comments are an important acknowledgment of the implicit male-dominated, and more so during this time certainly, sexist industry that female architects were operating in. Díaz, who has written what I am describing as feminist architectural histories of Cuba, notes that while Menéndez was referenced in Álbum de Cuba and the magazine, Arquitectura, this mention was because she was working alongside her husband (72).1 However, her work also evinces how these conditions, at least for the women in question, did not prevent them from producing valuable work.
After 1959 the couple left for Washington D.C., where they would stay for the rest of their lives, continuing to practice as architects for residential as well as commercial projects. In addition, Arroyo served on the U.S. Commission of Fine Arts from 1971-1976. Aside from the visible legacies they left behind on landscapes in both the U.S. and Cuba, their work features prominently in Eduardo Luis Rodríguez’s 2000 The Havana Guide: Modern Architecture (1925-1965). More recently, the couple’s work is featured on a digital map of twentieth-century Cuban architecture made, in the words of the co-creator Josef Asteinza, “for documenting and conserving the historic fabric of the twentieth-century city.”
Notes
- See also: Florencia Peñate Díaz, “Significado de la obra de las arquitectas cubanas Elana y Alicia Pujals Mederos / The significance of the work of Cuban architects Elena and Alicia Pujals Mederos.” Arquitectura y Urbanismo, vol. 37, no. 1, 2016, pp. 26-36.
Works Cited
Asteinza, Josef. “Mapping Cuba’s Twentieth-Century Architecture.” Association for the Study of the Cuban Economy, 30 Nov. 2016, www.ascecuba.org/asce_proceedings/mapping-cubas-twentieth-century-architecture/. Accessed 2 Dec. 2019.
Baez, Eduardo. Cruelty and Utopia: Cities and Landscapes of Latin America. Princeton Architectural Press, 2003.
Bruno, Guiliana. “Havana: Memoirs of Material Culture.” Journal of Visual Culture, vol. 2, no. 3, 2003, pp. 303-324.
Delson, Susan. “Preview: Cuban Architects at Home and in Exile: The Modernist Generation.” Cubanartnews, 25 October 2016. Accessed Nov. 23 2019.
Díaz, Florencia Peñate. “La obra de las arquitectas cubanas de la República entre los años 40 y fines de los 50 del siglo XX / The work of female Cuban architects of the Republic between the 1940s and the late 50s of the 20th century.” Arquitectura y Urbanismo, vol. 33, no. 1, 2012, pp. 70-82.
Escolano, Victor Pérez. “A European Glance in the Mirror of Caribbean Modern Architecture.” Translated by Isabelle Kite. Docomomo, no. 33, 2005.
Isla, Wilfredo Cancio. “Falleció Nicolás Arroyo, pionero del modernismo cubano / Nicolás Arroyo, pioneer of Cuban modernism, died.” el Nuevo Herald, 25 July 2008, www.elnuevoherald.com/ultimas-noticias/article1934191.html. Accessed Nov. 18 2019.
Perrottet, Tony. Cuba Libre! Che, Fidel, and the Improbable Revolution That Changed the World. Blue Rider Press, 2019.
Perur, Srinath. “The Habana Libre hotel, pawn in Castro's battle against the US - a history of cities in 50 buildings, day 34.” The Guardian, 12 May 2015, www.theguardian.com/cities/2015/may/12/havana-habana-libre-castro-cuba-us-history-cities-50-buildings-day-34. Accessed Nov. 18 2019.